By Futurist Thomas Frey
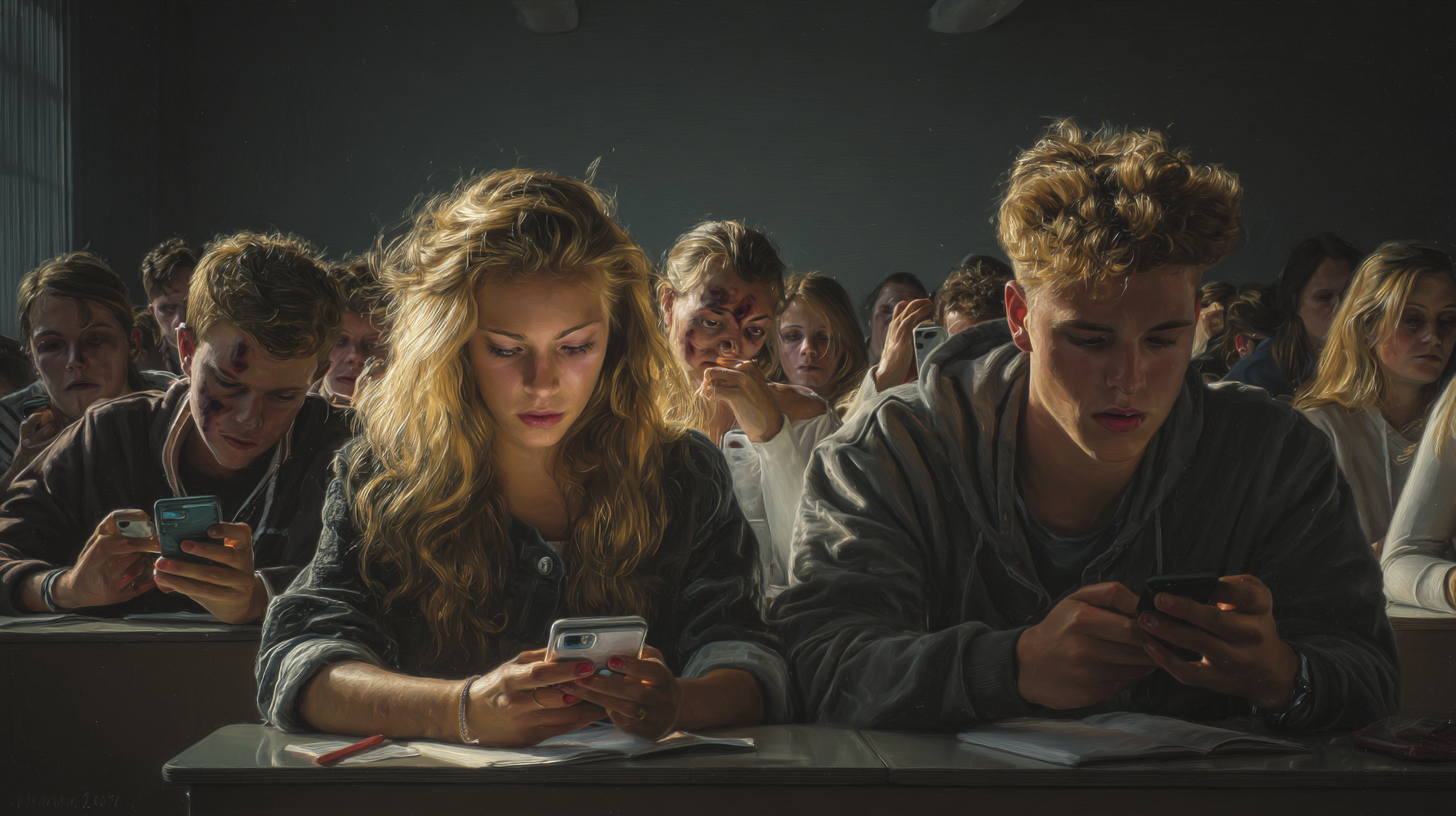
A generation is growing up tethered to their phones, not just by habit but by compulsion. By age 14, about a third of kids are already addicted to social media—a pattern linked to being 2–3 times more likely to report suicidal behaviors. Among young adults ages 18–22, the numbers climb higher, with 40% openly admitting they’re addicted.
Yet despite these alarming statistics, this crisis has barely penetrated mainstream awareness. We debate screen time limits, parental controls, or whether TikTok is rotting attention spans. But the real story is darker: social media is rewiring adolescent brains, creating behavioral dependencies that mirror gambling, drug use, and other recognized addictions—yet without the stigma or urgency that usually comes with the word “epidemic.”
Continue reading… “The Teen Social Media Addiction Epidemic: A Silent Crisis”