by Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
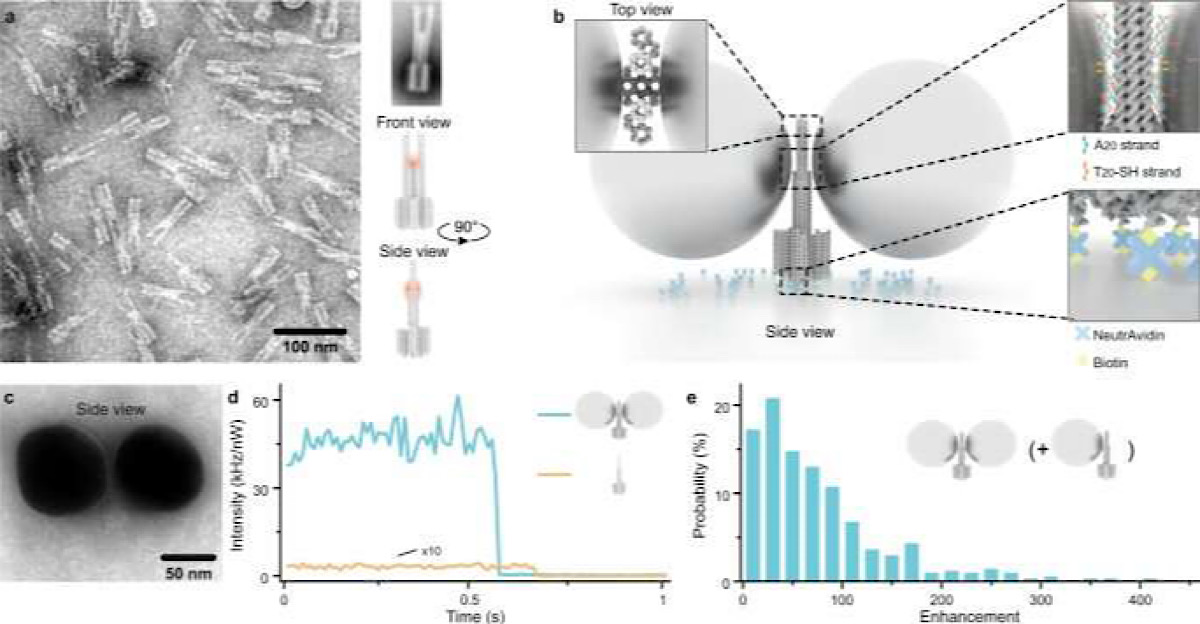
a TEM image (left, reproduced at least 3 times) and sketches (right) of the DNA origami structure used for the nanoantenna assembly with the position of the plasmonic hotspot indicated in red. A representative class averaged TEM image of the DNA origami used is shown on the upper right. b Schematics of NACHOS assembly: the DNA origami construct is bound to the BSA-biotin coated surface via biotin-NeutrAvidin interactions, thiolated DNA-functionalized 100 nm silver particles are attached to the DNA origami nanoantenna via polyadenine (A20) binding strands in the zipper-like geometry to minimize the distance between the origami and the nanoparticles30. c TEM image of a NACHOS with 100 nm silver nanoparticles (reproduced at least 3 times). d Single-molecule fluorescence intensity transients, measured by confocal microscopy, normalized to the same excitation power of a single Alexa Fluor 647 dye incorporated in a DNA origami (orange) and in a DNA origami nanoantenna with two 100 nm silver nanoparticles (blue) excited at 639 nm e. Fluorescence enhancement distribution of Alexa Fluor 647 measured in NACHOS with 100 nm silver nanoparticles. A total number of 164 and 449 single molecules in the reference (more examples are provided in Supplementary Fig. 3) and NACHOS structures were analyzed, respectively. Credit: Nature Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21238-9
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich researchers show that the light emitted by a single molecule can be detected with a low-cost optical setup. Their prototype could facilitate medical diagnostics.
Biomarkers play a central role in the diagnosis of disease and assessment of its course. Among the markers now in use are genes, proteins, hormones, lipids and other classes of molecules. Biomarkers can be found in the blood, in cerebrospinal fluid, urine and various types of tissues, but most of them have one thing in common: They occur in extremely low concentrations, and are therefore technically challenging to detect and quantify.
Many detection procedures use molecular probes, such as antibodies or short nucleic-acid sequences, which are designed to bind to specific biomarkers. When a probe recognizes and binds to its target, chemical or physical reactions give rise to fluorescence signals. Such methods work well, provided they are sensitive enough to recognize the relevant biomarker in a high percentage of all patients who carry it in their blood. In addition, before such fluorescence-based tests can be used in practice, the biomarkers themselves or their signals must be amplified. The ultimate goal is to enable medical screening to be carried out directly on patients, without having to send the samples to a distant laboratory for analysis.
Continue reading… “Detecting single molecules and diagnosing diseases with a smartphone”