While most satellites dutifully beam raw data back to Earth for humans to analyze, Φsat-2 has a different job: thinking.
Launched in August 2024, this compact cubesat—roughly the size of a shoebox—quietly crossed a major threshold this year. It didn’t just start sending images back to Earth. It began making decisions. Real decisions. About what matters, what doesn’t, and what needs our attention now.
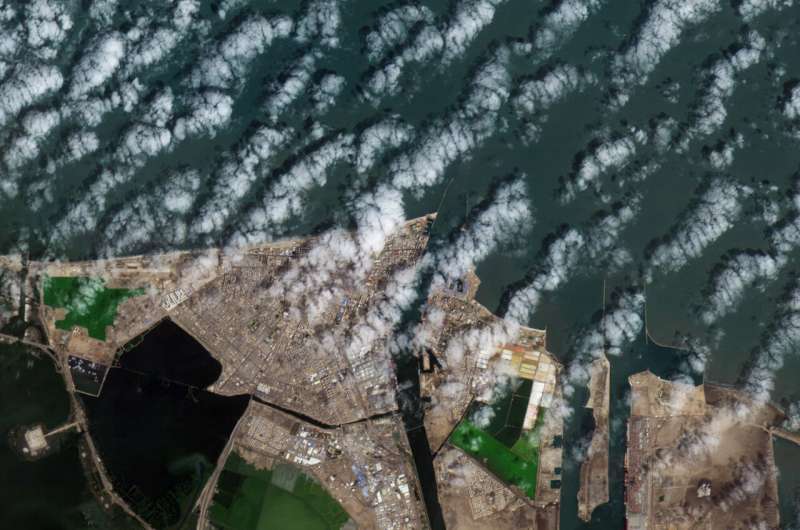
Orbiting 510 kilometers above us, Φsat-2 is equipped with AI powerful enough to sift through cloud-covered landscapes, ignore unusable images, and zero in on wildfire zones, oil spills, marine traffic, and even earthquake aftermath. It doesn’t wait for instructions. It triages. It prioritizes. It edits reality before we even see it.
Continue reading… “The Sky Is Thinking: Φsat-2 Ushers in the Era of Autonomous Earth Surveillance”